Just how healthy are your muscles and joints?
Answer our questions and find out if your flexibility is compromised.
Find out how flexible you arePsoas – so-what? The psoas (pronounced so-as) muscle is the only muscle in the body that connects your torso to your legs and actually has essential roles in our body movements. In this blog, I take a look at the importance of the psoas muscle, what it is, what it does and whether or not it can contribute to back pain.
The psoas muscles (pronounced so-as) are the primary connectors between your torso and your legs. The psoas muscle usually refers to a combination of two muscles; the iliacus and the psoas major muscle. Together these two muscles are better known as the iliopsoas muscle. There is a third muscle known as the psoas minor muscle which is found on the left side of the body. However, its role is so minimal that only around half of the population even have this muscle!
The psoas major and the iliacus muscles help to stabilise the spine and play a role in our posture, therefore weak psoas muscles can cause havoc in our body resulting in surrounding muscles overcompensating. Often when our psoas muscle is tight it can be responsible for other pains in the body such as lower back pain and pelvic pain.
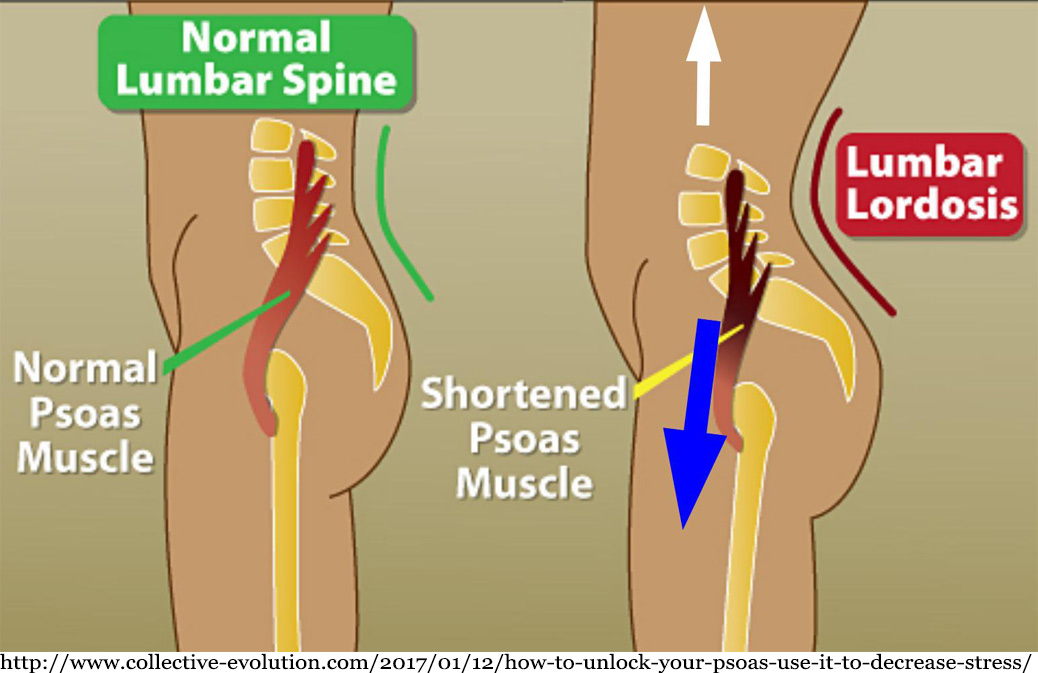
Structurally, your psoas muscles are the deepest muscles in your core and they are the only muscles that connect your spine to your legs. This means that they cross the hip joint which makes them extremely powerful hip flexors. They attach from your thoracic vertebrae (mid-spine) to your lumbar vertebrae (lower spine), through your pelvis and then finally attach to your femurs (thighbones).

• Connects our upper half of our body to our lower half
• It allows us to bend our hips and legs towards the chest
• Assist in moving the leg forward when we walk or run
• Plays a key role in our centre of gravity and controlling big body movements
• Strengthening the spine
• They flex our torso forward when we want to bend over
• They stabilise our torso and spine while sitting or in motion
• They support our internal organs such as the small intestine
The psoas muscles are not only important for our physical structure, but can even benefit our psychological well-being because of their connection to the breath. Two tendons for the diaphragm, the crura, connect to the spine alongside where the psoas muscles attach. The diaphragm and the psoas muscles are connected through fascia that also connects the other hip muscles.
These connections between the psoas muscle and the diaphragm connect your ability to walk and breathe, and even how you respond to fear and excitement because, when you’re stressed, your psoas muscle contracts. This means that our psoas muscle can have a direct influence on our fight or flight response!
There are many reasons that people can experience back pain and actually a tight psoas muscle is not one of the major offenders. Sitting for prolonged periods of time, not taking frequent exercise and being overweight are all lifestyle factors that overshadow the psoas muscle’s role in your back pain. However, that’s not to say that the psoas muscle doesn’t have at least a little role to play in lower back pain.
People who sit for prolonged periods of time can develop a tight psoas because their hip is constantly in a state of flexion. This can cause a shortening of the psoas muscle which can cause it to pull forward on our lower vertebrae and cause an anterior pelvic tilt that emphasises a hyperlordotic curve (increased arch in the lower back). As a result, this can put pressure on the intervertebral discs of our spine which can cause an increased risk of injury, pain and even alterations to the way that we walk and move.
• Move regularly – if you have a desk job make the time to get up and move repeatedly throughout your day
• Have good posture – whether you’re sitting or standing it’s important to watch out for your posture. Slouching can cause compression in the spine and can restrict our breathing
• Lose excess weight – shedding extra pounds can help to take the pressure off of your spine, heart and circulatory processes
• Herbal remedies – Devil’s claw can help to relieve muscle and joint pain, this herb can be found in our Atrosan tablets and can help to relieve excessive inflammation in the body
• Stretch – stretching can help to relieve tension in the psoas muscle and work through any muscle knots. Try this simple low lunge exercise shown in the video below
1 https://www.yoganatomy.com/psoas-resources/
2 https://www.drnorthrup.com/psoas-muscle-vital-muscle-body/
 Looking for a solution to to help relieve symptoms such as muscle and joint pain, backache, rheumatic pain and lumbago?
Looking for a solution to to help relieve symptoms such as muscle and joint pain, backache, rheumatic pain and lumbago?
Buy now from your local store.
“I have used these for several years and would not wish to be without them.”![]()
To find local independent stores in your area that sell Atrosan Devil’s Claw tablets, simply type your postcode below.
Answer our questions and find out if your flexibility is compromised.
Find out how flexible you areAs the A. Vogel Muscles and Joints advisor, I recommend Atrogel® for the effective relief from aches and pains.
Learn moreFoods such as red meat and dairy products and drinks such as caffeine and alcohol can all trigger inflammation which can increase muscle and joint pain.
Worst foods for muscle & joint painDiscover the story of Alfred VogelNature is just about the best thing we’ve got!